Common Reasons for Losing Teeth
Have you ever wondered what teeth you lose as you grow? Losing baby teeth is a natural part of childhood, but do you know which ones will be replaced by permanent adult teeth? In this article, we will explore the sequence of tooth loss and the importance of proper dental care during this crucial stage of development. Let's dive in and discover what teeth you can expect to lose and what to expect as your smile transforms.
Which teeth do not fall out and which do?
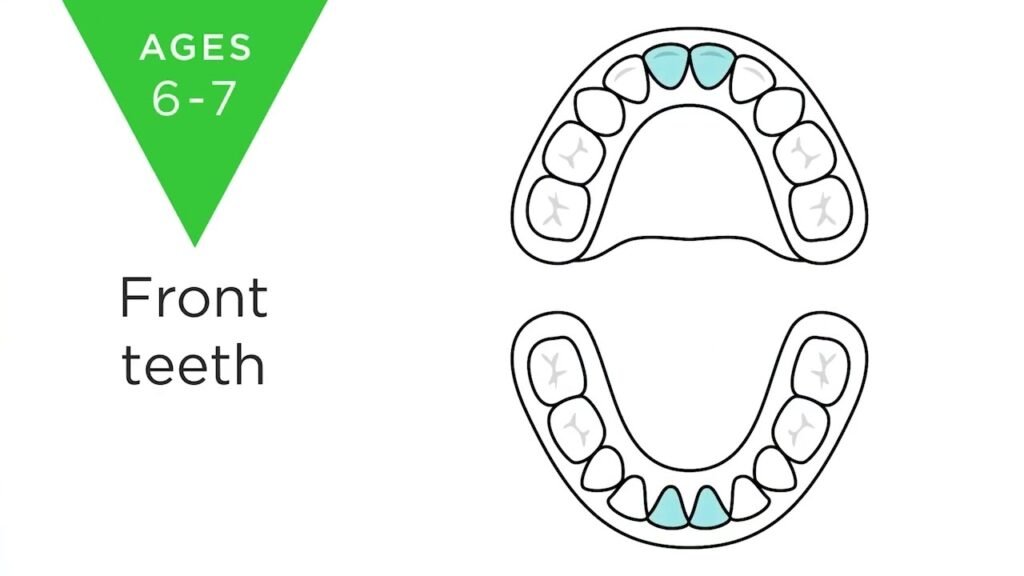
The shedding of baby teeth typically begins with the central incisors, followed by the emergence of permanent molars. As the process continues, the cuspid or second molar is usually the last to be lost, usually occurring around the age of 12. In total, a set of 32 permanent adult teeth will replace the baby teeth, completing the transition to a full adult dentition.
Do all 28 teeth fall out?
By the age of 12 to 14, children can expect to have lost all 28 of their baby teeth, making way for a full set of 32 adult teeth. This includes the wisdom teeth, which typically grow in towards the back of the mouth. It is a natural process of development and an important milestone in dental health.
Do all 20 teeth fall out?
Yes, all 20 of your primary teeth will eventually fall out to make way for your permanent teeth. These primary teeth are temporary placeholders until your permanent teeth develop. As you grow, your 32 permanent teeth, including your wisdom teeth, will replace the 20 milk teeth that you had as a child. Your wisdom teeth will emerge later in life, typically between the ages of 17 to 25, completing your set of permanent teeth without any milk teeth to replace.
In the natural process of tooth development, all 20 of your primary teeth will be shed to make room for your permanent teeth. As you age, your 32 permanent teeth, including your wisdom teeth, will fill in the spaces left behind by your milk teeth. Unlike your primary teeth, your wisdom teeth will not have any predecessors to replace, as they will erupt independently in your late teens or early twenties. This natural transition from primary to permanent teeth is a normal and essential part of dental development.
Prevent Tooth Loss: Understanding Common Causes
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential in preventing tooth loss. Neglecting to brush and floss regularly can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar, which can cause gum disease and ultimately result in tooth loss. Additionally, poor diet choices high in sugar and acids can contribute to tooth decay, weakening the structure of the teeth and increasing the risk of extraction.
Understanding the common causes of tooth loss can help individuals take proactive steps to preserve their oral health. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings can help detect early signs of gum disease and decay, allowing for prompt intervention to prevent further damage. By practicing good oral hygiene habits and making mindful dietary choices, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing tooth loss in the future.
Protect Your Smile: Reasons Behind Tooth Loss
Are you taking the necessary steps to protect your smile? Understanding the reasons behind tooth loss is essential for maintaining healthy teeth and gums. Poor oral hygiene, untreated gum disease, and inadequate dental care can all contribute to tooth loss. By prioritizing regular dental check-ups and practicing good oral hygiene habits, you can help prevent the potential loss of your teeth.
One of the leading causes of tooth loss is gum disease, which can be prevented with proper dental care. Neglecting to floss and brush regularly can lead to a buildup of plaque and tartar, eventually causing gum inflammation and infection. Without proper treatment, gum disease can progress to advanced stages, resulting in tooth loss. By maintaining a consistent oral care routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease and protect your smile for years to come.
Regular visits to the dentist are crucial for identifying and addressing any potential issues that could lead to tooth loss. Through routine cleanings and examinations, your dentist can detect early signs of decay, gum disease, or other oral health concerns. By addressing these issues promptly, you can prevent the need for extensive dental procedures and ultimately protect your smile from the potential of tooth loss. Don't wait until it's too late – take proactive steps to safeguard your teeth and maintain a healthy, confident smile.
Avoid Tooth Loss: Common Culprits Revealed
Are you worried about losing your teeth prematurely? Understanding the common culprits behind tooth loss is the first step in preventing this dental issue. Poor oral hygiene, gum disease, and tooth decay are often the main factors contributing to tooth loss. By practicing good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing and flossing regularly, and visiting your dentist for routine check-ups, you can help protect your teeth from these common culprits. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to maintaining a healthy and beautiful smile.
In addition to poor oral hygiene, other common culprits of tooth loss include smoking, poor nutrition, and untreated dental issues. Smoking can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of gum disease, which can ultimately lead to tooth loss. A diet high in sugar and acidic foods can also contribute to tooth decay and erosion, weakening the teeth over time. By avoiding these common culprits and making healthier choices for your oral health, you can significantly reduce the risk of tooth loss and enjoy a strong and confident smile for years to come.
In summary, understanding the sequence and timing of tooth loss in children is crucial for parents and caregivers to provide appropriate dental care and support. By knowing which teeth are expected to be lost at what age, individuals can better anticipate and address any potential concerns or issues that may arise. Ultimately, being informed about the natural process of tooth loss can help ensure the maintenance of good oral health and well-being for children as they transition into their adult teeth.