Understanding the Normal Age for Milk Teeth to Fall Out
Have you ever wondered at what age your child's milk teeth start to fall out? Understanding the timeline for this natural process can help parents prepare for the next stage of their child's dental development. In this article, we explore the typical age range for milk teeth to fall out and provide helpful tips for supporting your child through this important milestone.
Advantages
- Better oral health: As milk teeth fall out, it allows for permanent teeth to grow in properly, reducing the risk of overcrowding and misalignment.
- Improved speech development: Once milk teeth are replaced by permanent teeth, it can lead to clearer speech and improved communication skills.
- Enhanced aesthetics: The natural process of milk teeth falling out and being replaced by permanent teeth can lead to a more aesthetically pleasing smile.
- Increased confidence: Having a full set of permanent teeth can boost a child's confidence and self-esteem, leading to a more positive self-image.
Disadvantages
- Tooth decay: As children get older, milk teeth may be more prone to decay and cavities, leading to potential dental issues.
- Misalignment: If milk teeth do not fall out at the appropriate age, it can lead to misalignment of permanent teeth, causing potential orthodontic problems.
- Speech difficulties: Delayed loss of milk teeth can affect speech development and pronunciation in children.
- Social implications: Children may feel self-conscious or embarrassed if their milk teeth do not fall out at the same time as their peers, leading to potential social challenges.
- Pain and discomfort: If milk teeth do not fall out naturally and require intervention from a dentist, it can cause pain and discomfort for the child.
What is the maximum age for milk teeth to fall out?
The process of losing milk teeth is a common part of a child's development, with most children having a total of 20 milk teeth. These teeth typically start to emerge between 5 and 12 months of age and continue until around 3 years old. The natural shedding of milk teeth usually begins between 3 and 6 years old, with the entire process usually completed by the age of 12.
Is it typical for a 14-year-old to still have milk teeth?
It is not unusual for children to still have baby teeth at the age of 14, as not all children develop at the same rate. However, if a child is older than 14 and still has a significant number of baby teeth, it could be a sign of a potential issue that may need to be addressed by a dentist. It is important to monitor the situation and consult with a dental professional if necessary to ensure proper dental development and health.
What is the average age to lose milk teeth?
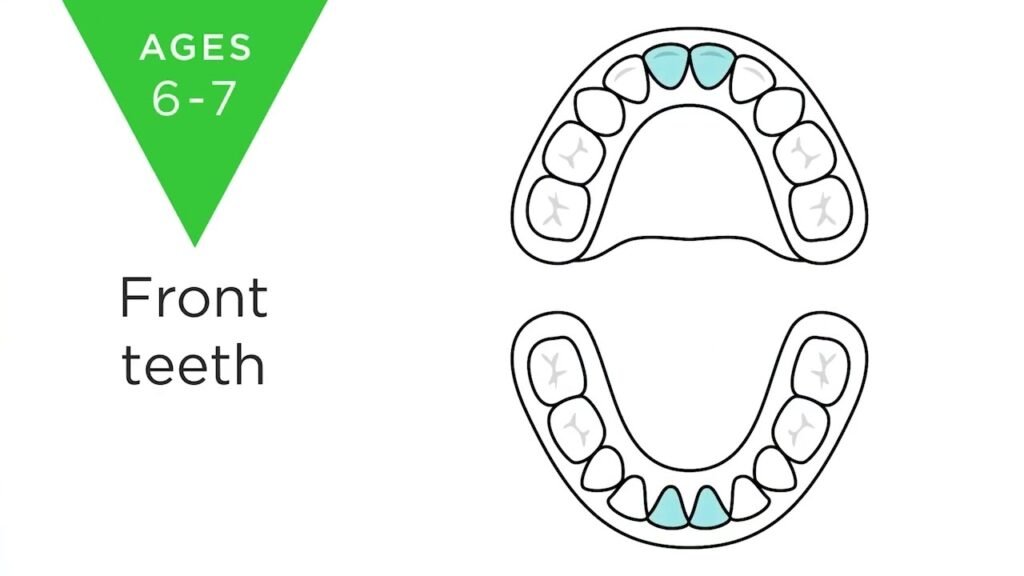
On average, children begin to lose their milk teeth around the age of six, starting with the lower and upper front teeth. This process is then followed by the eruption of the first big adult teeth at the back, known as the first permanent molars. The entire process typically concludes around the age of 12, when the last baby tooth is lost.
Demystifying the Natural Timeline of Baby Teeth Loss
As parents, it is natural to feel anxious about the process of baby teeth loss. Understanding the natural timeline of when and how children typically lose their baby teeth can help alleviate some of these worries. Around the age of 6, children typically start to lose their first set of baby teeth, with the process continuing until around the age of 12. This gradual transition from baby teeth to permanent teeth is a normal and healthy part of a child's development.
By demystifying the natural timeline of baby teeth loss, parents can better prepare themselves and their children for this inevitable phase. It is important to remember that every child is different, and variations in the timing of tooth loss are completely normal. Encouraging good oral hygiene habits and regular dental check-ups can help ensure a smooth and healthy transition for your child as they grow and develop.
A Parent's Guide to the Typical Shedding of Milk Teeth
As a parent, it's important to understand the typical shedding process of milk teeth in children. Around the age of 6 or 7, children begin to lose their baby teeth as their permanent teeth start to come in. This natural process can sometimes be accompanied by minor discomfort or bleeding, but it is usually nothing to worry about. Encouraging good oral hygiene habits and providing gentle care during this time can help make the transition smoother for your child.
It's essential to reassure your child that losing their baby teeth is a normal and necessary part of growing up. Make sure to celebrate each lost tooth as a milestone and encourage proper dental care to keep their new permanent teeth healthy. By understanding and supporting your child through the shedding process, you can help them feel confident and excited about their changing smile.
Overall, understanding the average age for milk teeth to fall out is essential for parents to monitor their child's dental development. By being aware of when these teeth typically shed, parents can ensure proper oral care and address any concerns with their child's dentist if necessary. Ultimately, staying informed and proactive in dental health can lead to a lifetime of healthy smiles.